Wonders of Neem Gum – A Review

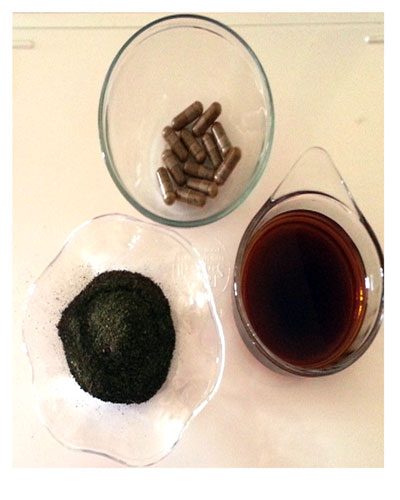
Neem (Azadirachta indica A Juss) gum is extracted from Neem tree by induced or natural injury. Neem gum is clear, bright and amber-coloured material non-bitter in taste and is soluble in cold water. Neem gum belongs to the family of galactan gums.
Studies by Nair et al (1985) found that any injury or application of ethephon and paraquat led to degradation of starch grains and cell wall, which in turn contributed to the overproduction of Neem gum.
Neem gum contains L-Arabinose, L-Fructose, D-Galactose, D-Glucoronic acid and traces of D-Xylose( Mukherjee S et al 1951) ; free sugars Glucose, Fructose, Mannose, Rhamnose and Xylose; Amino acids Alanine, Amino butyric acid, Arginine, Asparagines, Aspartic acid, Glycine, Norvaline, Praline, and Organic acids Citric acid, Malonic acid , Succinic acid and Fumaric acid. Neem gum has unusual structural features that it contains appreciable amount of D-glucosamine and proteins unlike other plant gums (Lakshmi SU et al, 1967). There is presence of at least two protein-rich components and two polysaccharide components in Neem gum. Neem gum contains 35% of proteinaceous material. The most abundant amino acid is aspartic acid; there are also considerable proportions of serine and threonine, and at least 2% of amino sugars (Nayak et al, 1978). Neem gum protease was characterised as a glycoprotein. The protease was found to be an N ?glycosidic bond involving glucosamine (Nayak et al, 1982).
Neem Gum is used as a stabilizing agent, gels and thickening agent. Neem Gum is used in soaps, tooth paste, tooth powders. It is used in antiseptic creams, tablet binder, and coater. It has been used in dyeing and printing of fabrics. It is widely used in South Asia as "Neem Glue."
The neem gum is mixed with beeswax and smeared on cracked feet.
Research Review
According to Abayomi Tolulope Ogunjimi et al, 2013, besides its medicinal uses, Neem gum has certain pharmaceutical applications. Co processing of Neem gum with two Excipient namely lactose and rice starch enhances the consolidation properties of the co processed Excipient. Co processing also improves the flow properties of the novel co processed Excipient.
According to a study done by M.G.L.Annaamalai et al in 2015, the purest kind of Neem Gum can be used in concrete mixes as a natural compressive strength enhancer. Neem Gum offers compressive strength significantly greater than normal concrete at the optimum amount of 1.2% of Neem Gum.
A study done by Rishabha Malviya et al in 2017 showed that Neem gum can be used as an emulsifying agent with a significant antioxidant potential in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industry. So Neem gum can attract worldwide manufacturer as substitute of other emulsifying agent.
Manju Nagpal et al, 2017 studied to improve bioavailability of Aceclofenac using neem gum as water soluble carrier for the development of solid dispersion based dosage form of the drug. Inclusion of NMG improved the balance between binding and disintegration properties of paracetamol tablets. Neem gum produced paracetamol tablets with lower disintegration and dissolution times. The solubility, drug release and in vivo results suggested applicability of neem gum as a prospective carrier of poorly soluble drugs.
Based on the findings by Chinnaperumal Kamaraja et al 2017, Neem gum nano formulation (NGNF) could provide an important new control product to reduce populations against Helicoverpa Armigera and Spodoptera litura. Chemical analyses revealed ten compounds in NGE, and these potentially provide novel and environmental friendly approach that NGNF could be used as an agent to prepare novel bio-pesticides formulations.
Corrosion mitigation of carbon steel (CS) by Neem gum (Gum exudates of Azadirachta indica, GAI) was investigated in 1N HCl medium by M. Malarvizhi et al, 2018. GAI showed significant corrosion inhibition for CS in hydrochloric acid medium.
Uses of biopolymers for the development of nanocarriers are receiving significant attention due to its biocompatible and biodegradable nature. Neem gum coated superparamagnetic nanoparticle based novel nanobiocomposite (Fe3O4@NG NBC) has low toxicity, with good biodegradability and water dispersability. It has an excellent drug loading ability and good magnetic controllability. It could offer potential applications in biomedical field including targeted drug delivery for cancer diagnosis and treatment in near future (Khushnuma Asghar et al, 2019).
The research study “Neem gum based pH responsive hydro gel matrix: A new pharmaceutical Excipient for the sustained release of anticancer drug” done Priyanka Mankotia et al, 2019 was aimed to synthesize neem gum-based site-specific drug delivery device for anticancer drug methotrexate at different pH condition. Results indicate that the synthesized polymers are biocompatible with all blood groups. Due to Neem gum’s natural availability, non-toxicity, biocompatibility, water dispersability and the abundance of functional groups/bioactive phytochemicals makes it an efficient material for drug delivery applications.
In the study done by Abhishek Dhar et al, 2019, on neem tree gum consisting of bio electrolyte and bio electrode was fabricated for flexible energy storage device. The novelty of the present was that naturally occurring neem gum can be an unprecedented green resource for bio electrochemical flexible energy storage device with remarkably high stability under strong mechanical bent and long?term charging?discharging cycles of the fabricated device.
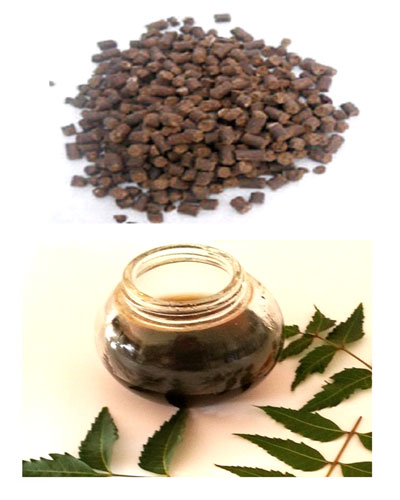
Neem Amber colored gum

References:
Abayomi Tolulope Ogunjimi, Gbenga Alebiowu; Flow and consolidation properties of neem gum co processed with two pharmaceutical Excipient; Powder Technology, 2013; 246,187-192
Abhishek Dhar, Nadavala Siva Kumar, Mehul Khimani, Ahmed S. Al?Fatesh, Ahmed A. Ibrahim , Anish H. Fakeeha, Poonam Bhadja , Rohit L. Vekariya; Naturally occurring neem gum: An unprecedented green resource for bio electrochemical flexible energy storage device; International Journal of Energy Research,2019; Volume 44, Issue 2
Chinnaperumal Kamaraj, Pachiyappan Rajiv Gandhi, Gandhi Elango, Sengodan Karthi, Ill-Min Chung, Govindasamy Rajakumar; Novel and environmental friendly approach; Impact of Neem (Azadirachta indica) gum nano formulation (NGNF) on Helicoverpa armigera (Hub.) and Spodoptera litura (Fab.); BIOMAC, 2017; 8138, No. of Pages 11
Khushnuma Asghar, Mohd Qasim, Dibakar Das; Synthesis and characterization of neem gum coated superparamagnetic nanoparticle based novel nanobiocomposite; Ceramics International,2019; 45(18)
Lakshmi SU, Pattabiraman TN; Studies on plant gums: I--Identification of nitrogenous compounds in neem (Azadirachta indica) gum and isolation of D-glucosamine; Indian Journal of Biochemistry, 01 Sep 1967, 4(3):181-183
Manju Nagpal, Geeta Aggarwal, Pratima Sharma, Paramjot Mahan, Gurjeet Singh Thakur; Neem Gum Based Solid Dispersion in Development of Aceclofenac Tablet with Enhanced Bioavailability; Drug Delivery Letters, 2017;Volume 7 ,
M.G.L.Annaamalai, G.Maheswaran, R.Yuvaraja, R.Jayakodi; Effect of Partial Replacement of Cement with Neem Gum on the Strength Characteristics of High Performance Concrete; International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2015; Vol.8, No.1, pp 178-183
M. Malarvizhi and J. Mallika; Efficacy of Corrosion Inhibitive Properties of Gum Exudates of Azadirachta Indica on Carbon Steel in 1N Hydrochloric Acid; Oriental Journal of Chemistry, 2018; Volume 34, Number 5
Mukherjee S, Srivastava HC; Structure of the neem (Azadirachta indica) gum; Curr Sci. 1955; 20(5):127?128.
Nayak B Ramakrishna, Radhakrishna Rao & T N Pattabiraman; Studies on plant gums. Isolation and characterisation of the major polysaccharide from Neem (Azadirachta indica) gum; Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences - Section B volume 87, pages261–269(1978)
Nayak B Ramakrishna , Thillaisthanam, N Pattabiraman; Studies on plant gums: Characterisation of neem (Azadirachta indica) gum protease as a glycoprotein; Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 1982; Volume 33, Issue 3
Nair MN B, J R Bhatt & J J Shah; Induction of traumatic gum cavities in sapwood of neem (Azadirachta indica A.Juss.) by ethephon and paraquat; Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 1985; 23: 60–62.
Priyanka Mankotia, Sonal Choudhary, Kashma Sharma, Vijay Kumar, Jaspreet Kaur Bhatia,
Ankush Parmar, Shweta Sharma, Vishal Sharma; Neem gum based pH responsive hydrogel matrix: A new pharmaceutical Excipient for the sustained release of anticancer drug; International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 142 (2020) 742–755
Rishabha Malviya, Pramod Kumar Sharma and Susheel Kumar Dubey; Antioxidant Potential and Emulsifying Properties of Neem (Azadirachta indica, Family Meliaceae) Gum Polysaccharide; Pharm Anal Acta 2017, 8:9
Dr Nirrmala Kotharii
Director & General Secretary, World Neem Organisation
Managing Director, Neem Wave Exhibitions LLP